The sequence and hence structure and function of proteins and nucleic acids. Other monosaccharides are used to form long fibers which can be used as a form of cellular.
Iii Carbohydrates Structures And Types A Guide To The Principles Of Animal Nutrition
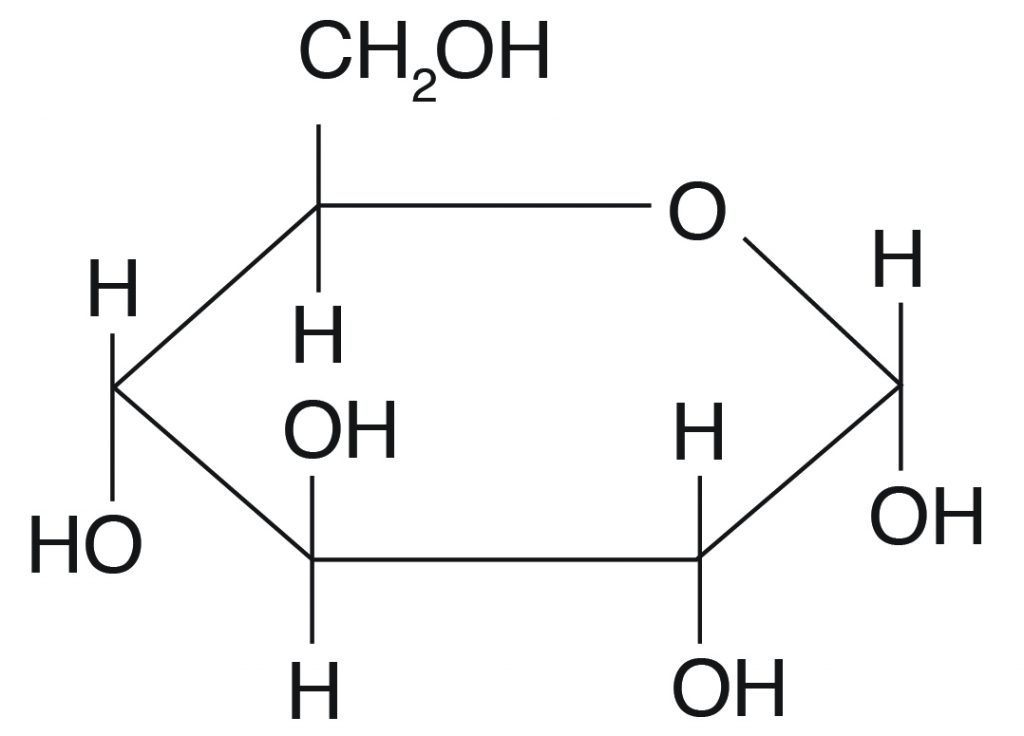
Five carbon atoms and one oxygen atom belonging to the aldehydic functional group make the corners or angles of the hexagon.

. The three components of a deoxyribonucleotide are a five-carbon sugar called deoxyribose a phosphate group and a nitrogenous base a nitrogen-containing ring structure that is responsible for complementary base pairing between nucleic acid strands Figure 1. Because only the base differs in each of the four types of subunits each polynucleotide chain in DNA is analogous to a necklace the backbone strung with four types of beads the four bases. It is a simple sugar having a molecular formula C 6 H 12 O 6.
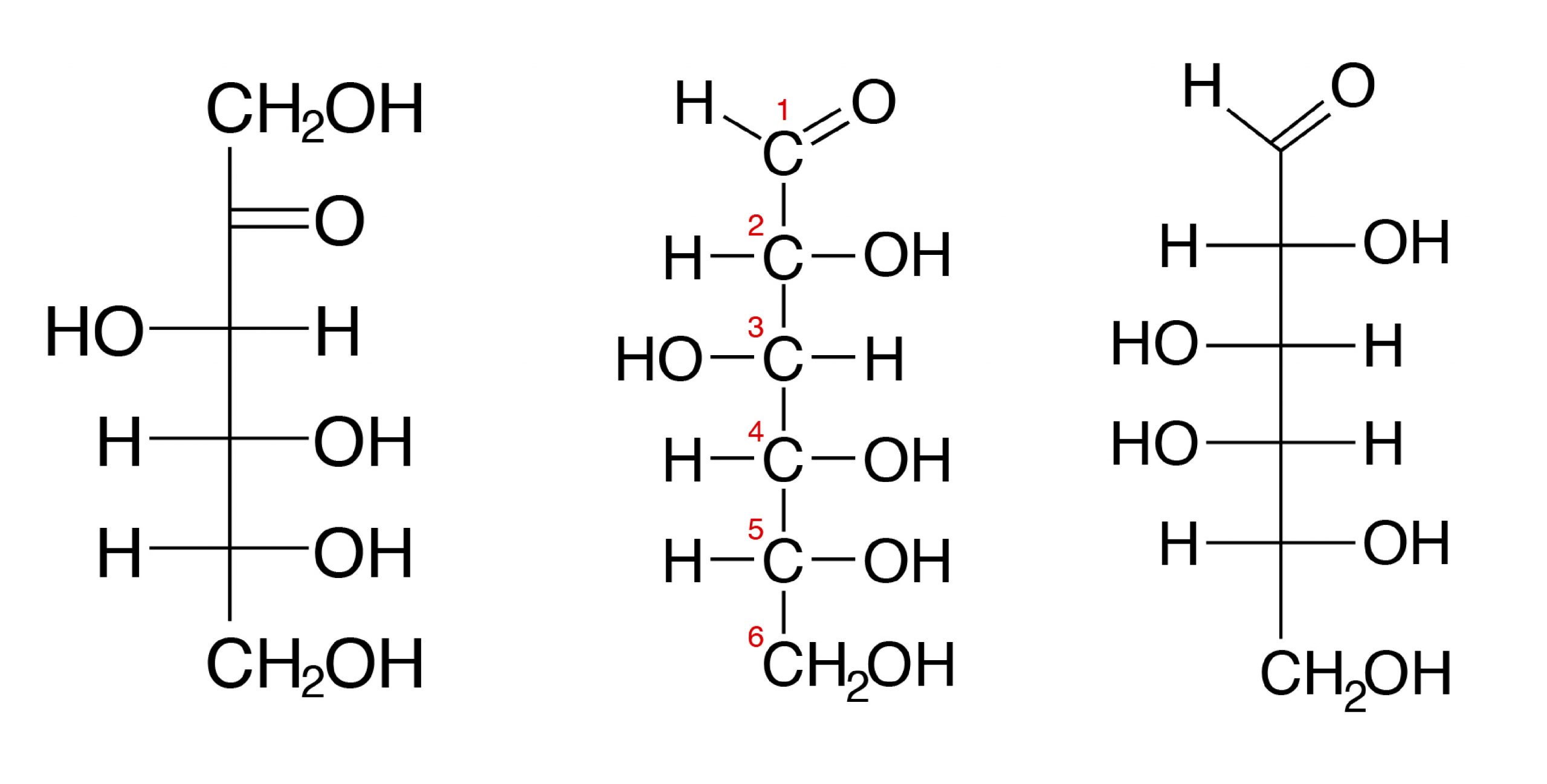
The primary or first carbon of the sugar links to the base. Sugars that bond via an alpha 14 linkage may be digested by mammalian enzymes. The formula for glyceraldehyde is C 3 H 6 O 3.
A polysaccharide is a large molecule made of many smaller monosaccharides. C n H 2n O n. Condensation reactions link carbon atom 1 to carbon atom 4 on the next β glucose.
Their Structures and Stereochemistry. It is the source of energy in cell function and the regulation of its metabolism is of great importance see fermentation. Sugar coat that surrounds the cells.
Sugar as a preservative by acting as a humectant maintaining and stabilising the water content in foods sugar helps to prevent or slow the growth of bacteria moulds and. Bundles of fibrils that arise at the ends of the cell beneath an outer sheath and spiral around the cell. The number 5 carbon of the sugar bonds to the phosphate group.
Describe the basic structure and function of sugars. This can react with water to make the simplest sugar glyceraldehyde but most couples to form glucose. The carbon atoms of the five-carbon deoxyribose are numbered 1ʹ 2ʹ 3ʹ 4ʹ and 5ʹ 1ʹ is read as one prime.
A polysaccharide can be a homopolysaccharide in which all the monosaccharides. Sugars link together via a glycosidic bond to form di- two monosaccharides or oligo- 3 to 15 monosaccharides and polysaccharides. The glucose subunits in the chain are oriented alternately upwards and downwards.
We know from VSEPR that the first carbon atom with only 3 bonds and no lone-pairs must have its bonds all in one. Cellulose is a polymer of β glucose - its made of long unbranched chains of beta-glucose. If the sugar has an aldehyde group the functional group with the structure R-CHO it is known as an aldose and if it has a ketone group the functional group with the structure RCOR it is known as a ketose.
Sugar helps to stop cookies and biscuits from obtaining surface cracking and helps give many cakes their lightness by interacting with egg proteins to help stabilise the whipped foam structure of the batter. Glucose is a widely available monosaccharide and is also known as dextrose and blood sugar. Produces a movement for spirochetes.
A five-carbon sugar pentose sugar a phosphate group PO 4 3- The bases and the sugar are different for DNA and RNA but all nucleotides link together using the same mechanism. Monosaccharides are simple sugars like glucose. Carbon oxygen and hydrogen.
However only the simple sugars or monosaccharides fit this formula exactlyThe other types of carbohydratesoligosaccharides and polysaccharides are based on the monosaccharide units. In general the formula for all simple sugars has this same ratio of carbon hydrogen and oxygen. A polysaccharide is also called a glycan.
Glucose fructose and galactose and the double sugars called disaccharides eg. Glucose from Greek glykys. The most common sugars found in foods are the single sugars called monosaccharides eg.
Sweet has the molecular formula C6H12O6. Filamentous appendage to give motility. Covalent bonds and polarity bond rotations and vibrations non-covalent interactions the hydrophobic effect and dynamic aspects of molecular structure.
Monosaccharides are the simplest form of sugar and the most basic units of carbohydrates. Monosaccharides have many functions within cells. Name three polysaccharides and describe their functions.
Special enzymes bind these small monomers together creating large sugar polymers or polysaccharides. When the word carbohydrate was coined it originally referred to compounds of the general formula CnH 2 On. This ring structure of glucose is known as glucopyranose.
Explore the definition with examples of monosaccharides and learn about their structure including the. The nucleotides are covalently linked together in a chain through the sugars and phosphates which thus form a backbone of alternating sugar-phosphate-sugar-phosphate see Figure 4-3. Glucose makes a ring when it is dissolved in an aqueous solution.
Glycogen- a chain of glucose in animals broken down when glucose is needed for energy. It is found in fruits and honey and is the major free sugar circulating in the blood of higher animals. Glucose is mainly manufactured by plants and most of the algae during the process of photosynthesis.
Most organisms create energy by breaking down the monosaccharide glucose and harvesting the energy released from the bonds. Sugars are the basic building blocks of carbohydrates found in nature. First and foremost monosaccharides are used to produce and store energy.
They can be found in milk tree saps such as maple syrup and many fruits and vegetables. In simple terms we can say that it is made up of six carbon atoms twelve hydrogen atoms and six oxygen atoms. The structure and hence function of macromolecules is governed by foundational principles of chemistry such as.
The ring formed by glucose is hexagonal in structure. The nature of glycosidic bonds influences the structural and chemical properties of the sugars and influences their ease of digestion. Starch- A chain of glucose in plants broken down when glucose is needed for energy.

What Are Carbohydrates Structure Function Expii

Carbohydrate Structure Formula Types What Are Carbohydrates Video Lesson Transcript Study Com

Carbohydrate Structure Formula Types What Are Carbohydrates Video Lesson Transcript Study Com
Iii Carbohydrates Structures And Types A Guide To The Principles Of Animal Nutrition
0 Comments